Learn all about Guillemin Links
What are they?
Guillemin bonds are a symmetrical coupling system, meaning that both halves are identical.
Guillemines have locking rings to connect and secure the other half. This is the French standard for cistern connections. They are used for both pumping and suction of liquids and solids such as powders and granules.
Characteristics
The main characteristics of the Guillemin links that Disumtec has are:
-
They are available in 316 stainless steel, aluminum, bronze or polypropylene.
-
In sizes ranging from DN50 to DN150
-
For male and female thread hoses
-
Ideal for working under pressures up to 240 PSI (16 bar)
-
Smooth surfaces help prevent product buildup
-
Easy to connect - They comply with Spanish regulations EN14420-8 and French regulations NF E-29572.
Applications
Guillemin links are used in a wide range of applications including:
-
Fluid Transfer: Guillemin couplings are used to connect hoses to tankers, silos and other fluid transfer equipment.
-
Civil Engineering: Guillemin couplings are used in construction to connect hoses to pumps, concrete mixers and other construction equipment.
-
Food Industry: Guillemin couplings are used in the food industry to connect hoses to packaging machines, food processing equipment and other food handling equipment.
How does it work?
The Guillemin coupling is connected by simply pushing the two halves together and turning a locking ring which fits into a channel in the other half of the coupling making a tight and secure connection. The couplings can be closed by hand or with the aid of specially designed wrenches. The standard material for the guillemins is Aluminium and Stainless Steel with optional sealing rings in white EPDM, Viton, NBR and Kalrez on request. The couplings are also available without the locking ring although this must be present on at least one of the halves to enable the connection.
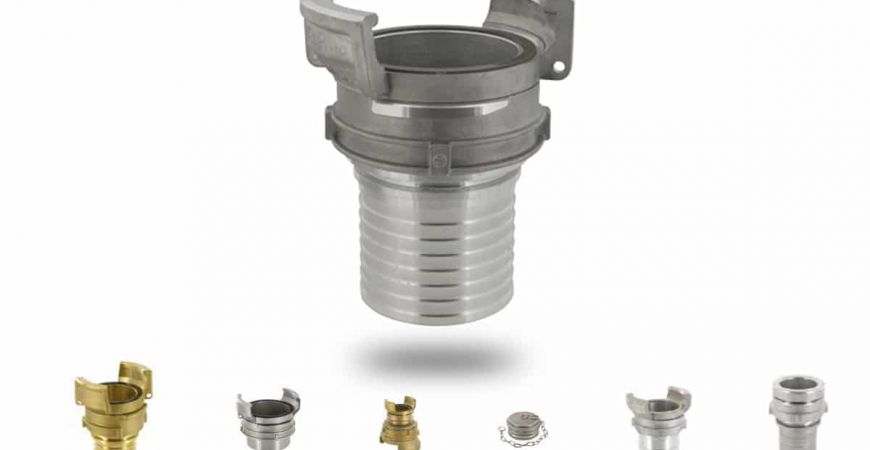
Below we show some of the most commonly used guillemins: guillemin with spike, guillemin with male thread, guillemin with female thread, etc.


.jpg)
.jpg)
%20(1).jpg)
.png)